Action Potentials At A Chemical Synapse Travel
In a chemical synapse a synaptic gap or cleft separates the pre- and the postsynaptic cells. The junction at which the electrical signal is converted.

Chemical And Electrical Synapses Biology For Majors Ii
The impulse generated in the neuron is transmitted in the form of an electrical signal or action potential which gets converted into a chemical synapse to transmit the signal from one synapse to another synapse.

Action potentials at a chemical synapse travel. An action potential is caused by either threshold or suprathreshold stimuli upon a neuron. In contrast in an electrical synapse the impulse travels in both directions. Different types of neurons use different neurotransmitters and therefore have different effects on their targets.
The sodium channels play a role in generating the action potential in excitable cells and activating a transmission along the axon. An action potential propagated to the axon terminal results in the secretion of chemical messengers called. An action potential nerve impulse is a rapid electrical signal that travels down a single cell.
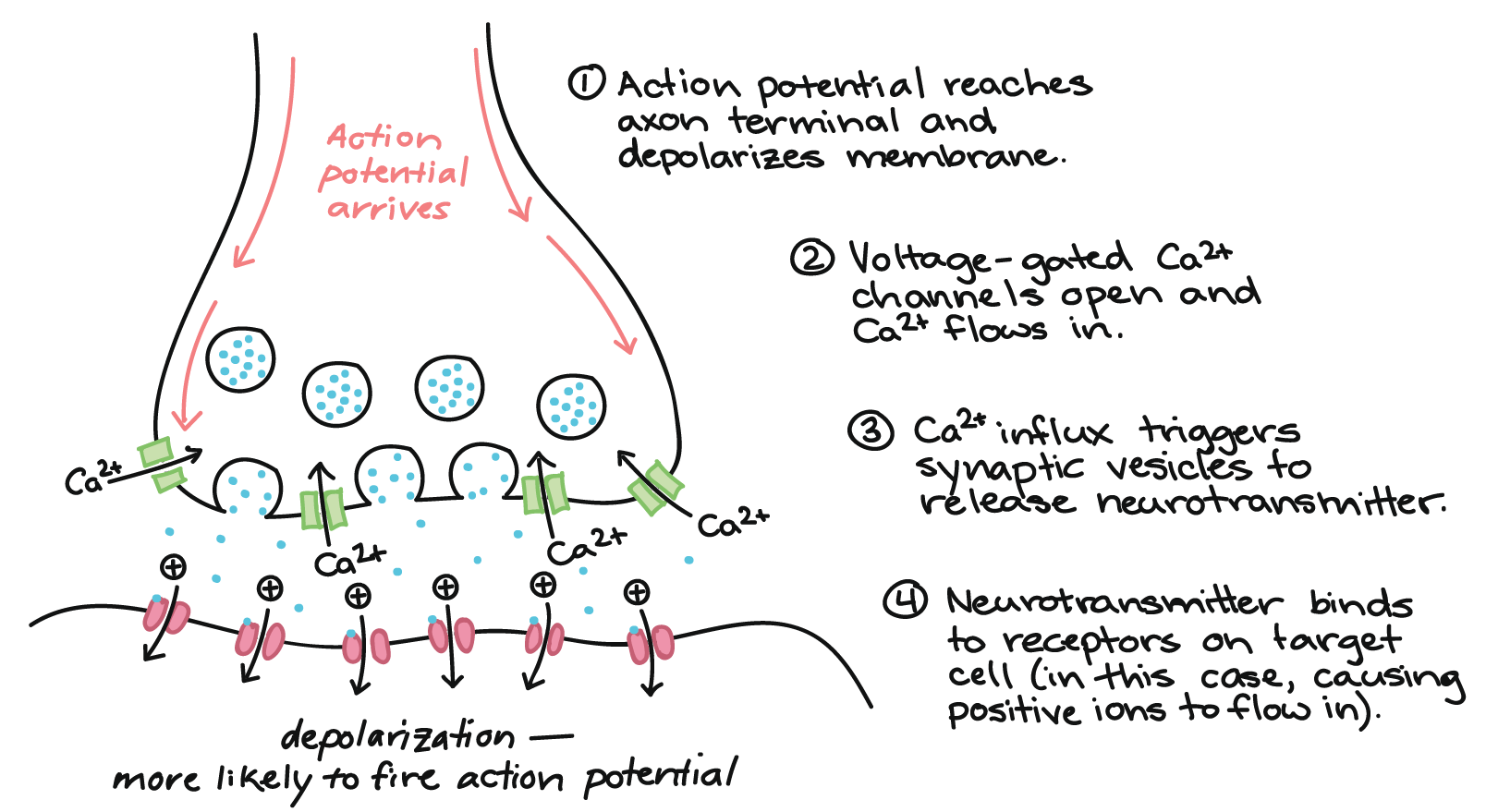
In a chemical synapse a nerve impulse can travel in only one direction. Chemical synapses comprise most of the synapses in your body. 1When an action potential depolarizes the plasma membrane of the synaptic terminal it 2 opens voltage-gated calcium channels in the membrane triggering an influx of Ca.
These action potentials cause the release of a chemical messenger from a storage vesicle in the axon terminal. Voltage-gated Ca2 channels open Ca2 enters axon terminal. Travel back and forth from presynaptic terminal to postsynaptic membrane.
The neurotransmitter travels across the synapse to excite or inhibit the target neuron. This means that neurons always fire at their full strength. Hypopolarization depolarization overshoot and repolarization.
Solution for Action potentials at a chemical synapse travel from presynaptic terminal to postsynaptic membrane. Action potentials are transmitted on a one-to-one basis at both a neuromuscular junction and a synapse. Ca2 entry causes neurotransmitter-containing synaptic vesicles to.
3 The elevated Ca concentration in the terminal causes synaptic. When an action potential is received to the terminal of the pre-synaptic membrane the voltage-gated calcium channels of the pre-synaptic membrane are opened. There is no such thing as a partial firing of a neuron.
Action potential arrives at axon terminal. This principle is known as the all-or-none law. Voltage gated sodium channel outside the cell is positive inside negative and the sodium channel opens Stages of Action Potential.
Chemical Synapse The synaptic cleft is filled with interstitial fluid. The chemical messenger called a neurotransmitter travels across a synapse. An action potential travels the length of the axon and causes release of neurotransmitter into the synapse.
Action potentials at a chemical synapse bartleby. Neurotransmitter A chemical released from a neuron following an action potential. Travel from presynaptic terminal to.
When an action potential reaches the axon terminal it depolarizes the membrane and opens voltage-gated Na channels. Travel from presynaptic terminal to postsynaptic membrane. The neurotransmitter travels across the synapse to excite or inhibit the target neuron.
So when an action potential depolarizes the membrane the leading edge activates other adjacent sodium channels. It consists of four phases. The action potential and consequent transmitter release allow the neuron to communicate with other neurons.
Just so why does the action potential move in one direction. Action potentials either happen or they dont. Na ions enter the.
Action potentials at a chemical synapse A. Action potentials occur when the graded potential reaches the threshold Compared to the inside of the resting plasma membrane the outside surface of the membrane is. Neurotransmission at a chemical synapse begins with the arrival of an action potential at the presynaptic axon terminal.
The long tail-like structure growing out of the cell body of a neuron that carries action potentials to send information to the synapse is known as the. They are all about the movement of ions Cell membrane in action potential. 1 Synaptic input makes membrane potential less and less negative Na sodium channels open and Na rushes into cell and makes cell inside more positive K potassium channels open completely and K streams.
Travel from postsynaptic membrane to presynaptic Answered. Travel from postsynaptic membrane to presynaptic terminal. An action potential travels the length of the axon and causes release of neurotransmitter into the synapse.
An action potential propagates along the cell membrane of an axon until it reaches the terminal button. The Synapse Neurons generate action potentials which consist of brief reversals in the polarity electrical state of the axon transmitting region of the cell.

Do Electrical Synapses Transmit Signals Faster Than Chemical Synapses Due To Action Potential Quora
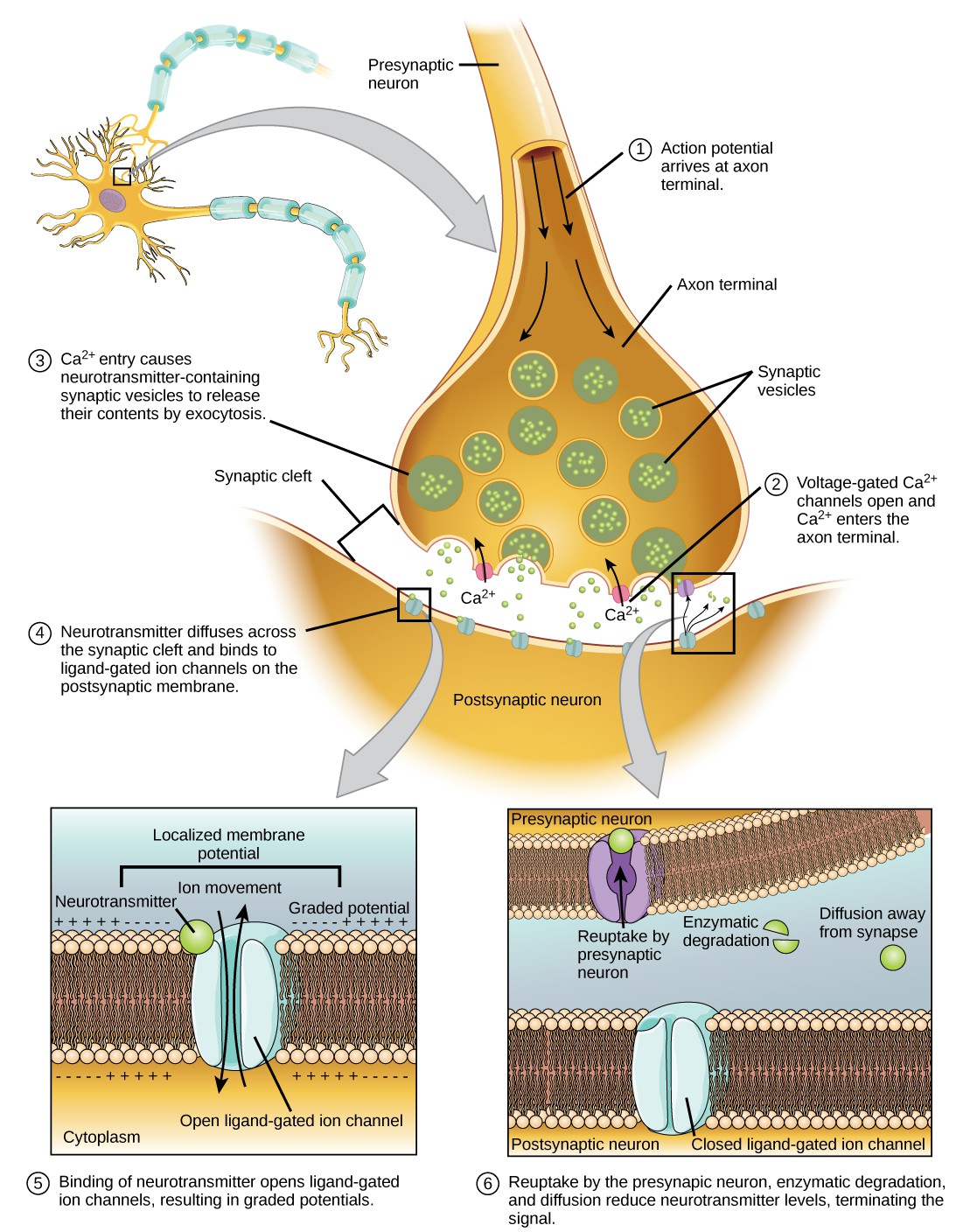
How Neurons Communicate Openstax Biology
16 2 How Neurons Communicate Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
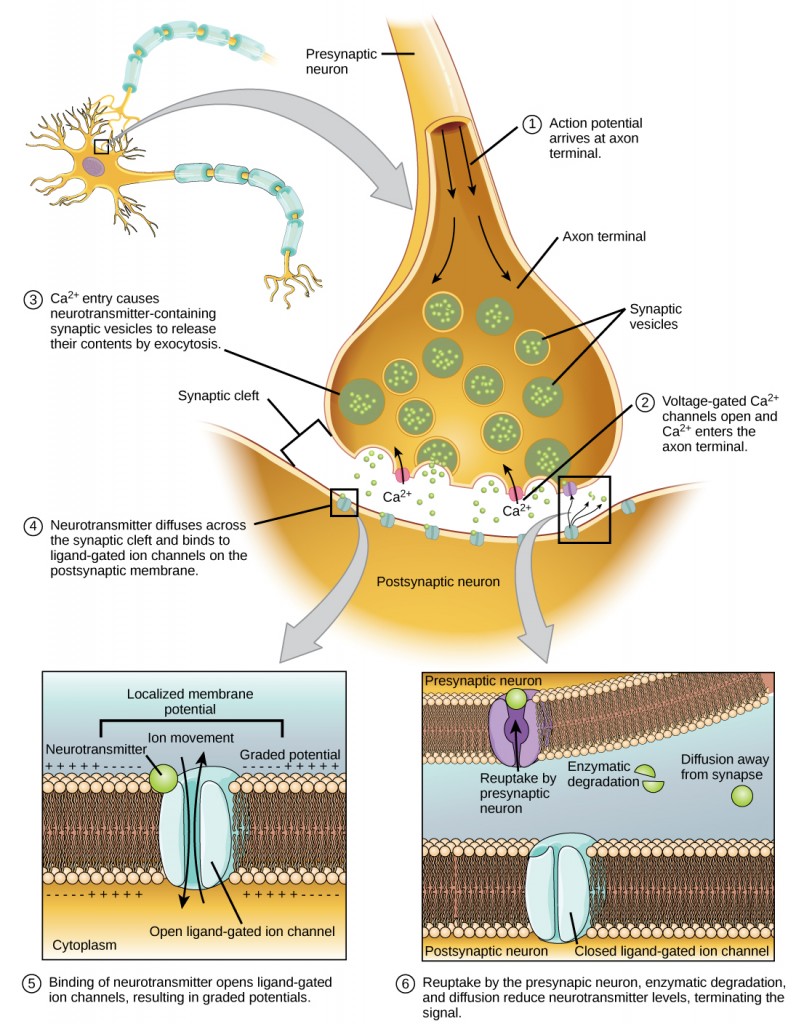
16 2 How Neurons Communicate Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
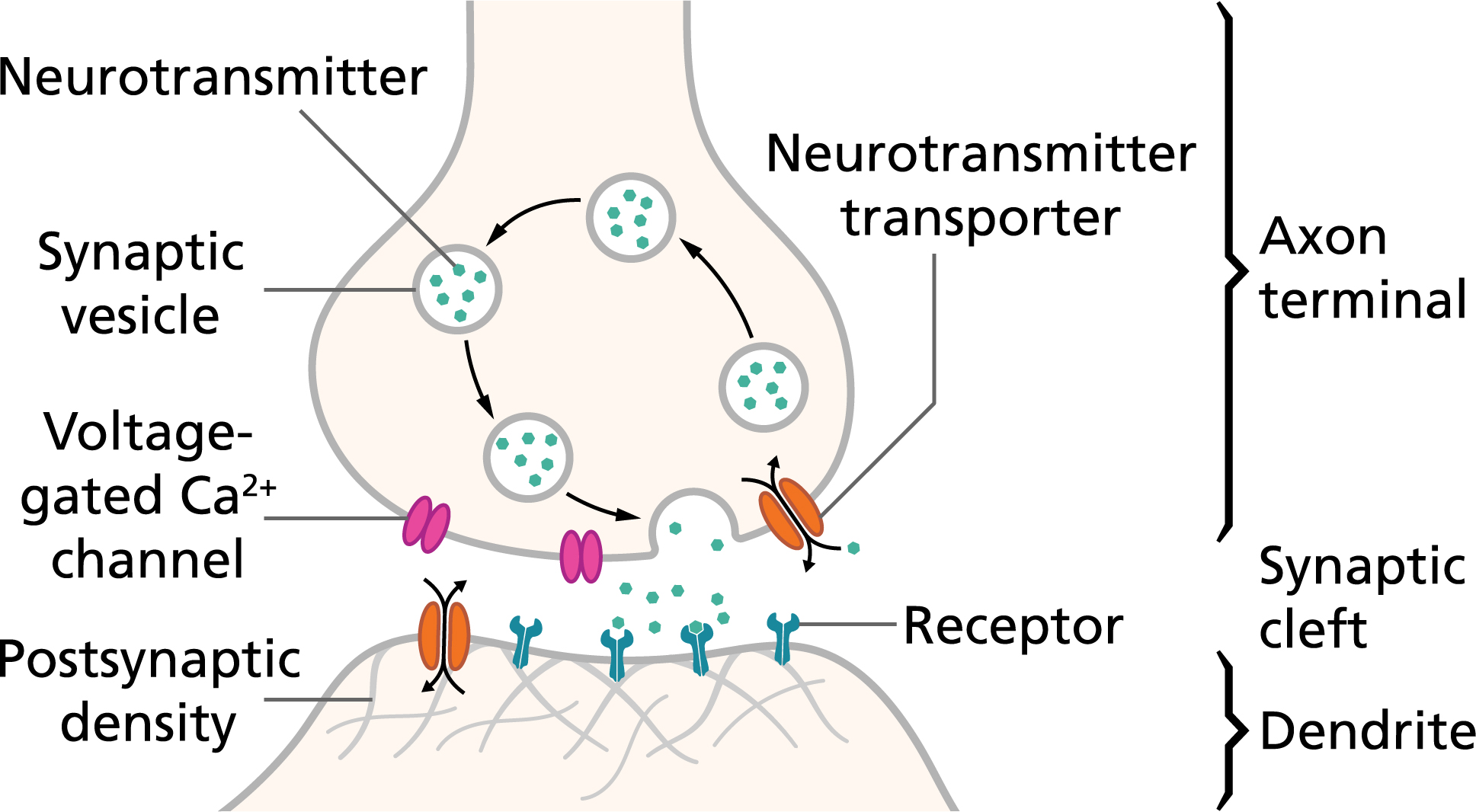
Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland

How Neurons Communicate Boundless Biology
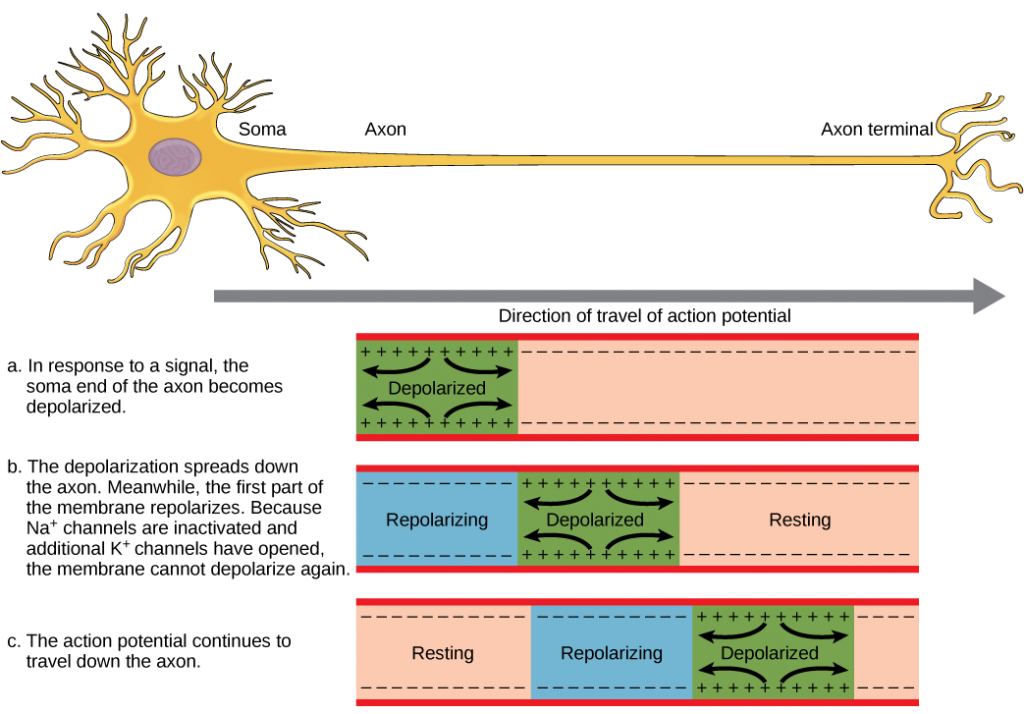
16 2 How Neurons Communicate Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition